在大小为n x n的网格grid上,每个单元格都有一盏灯,最初灯都处于关闭状态。
给你一个由灯的位置组成的二维数组lamps,其中lamps[i] = [rowi, coli]表示打开位于grid[rowi][coli]的灯。即便同一盏灯可能在lamps中多次列出,不会影响这盏灯处于打开状态。
当一盏灯处于打开状态,它将会照亮自身所在单元格以及同一行、同一列和两条对角线上的所有其他单元格。
另给你一个二维数组queries,其中queries[j] = [rowj, colj]。对于第j个查询,如果单元格[rowj, colj]是被照亮的,则查询结果为1,否则为0。在第j次查询之后按照查询的顺序 ,关闭位于单元格grid[rowj][colj]上及相邻 8 个方向上(与单元格grid[rowi][coli]共享角或边)的任何灯。
返回一个整数数组ans作为答案,ans[j]应等于第j次查询queries[j]的结果,1表示照亮,0表示未照亮。
示例 1:
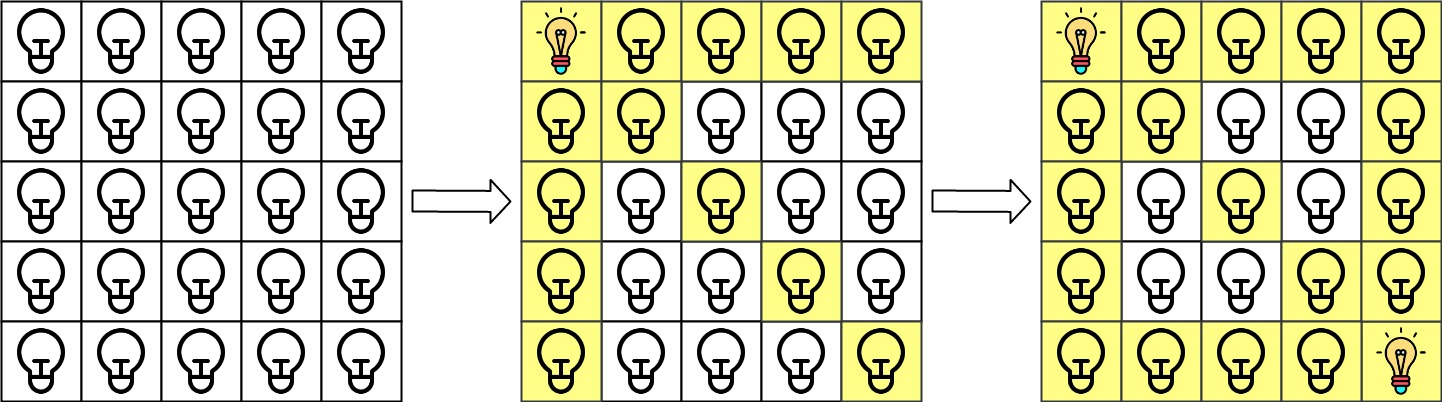
输入:n = 5, lamps = [[0,0],[4,4]], queries = [[1,1],[1,0]]
输出:[1,0]
解释:最初所有灯都是关闭的。在执行查询之前,打开位于 [0, 0] 和 [4, 4] 的灯。第 0 次查询检查 grid[1][1] 是否被照亮(蓝色方框)。该单元格被照亮,所以 ans[0] = 1 。然后,关闭红色方框中的所有灯。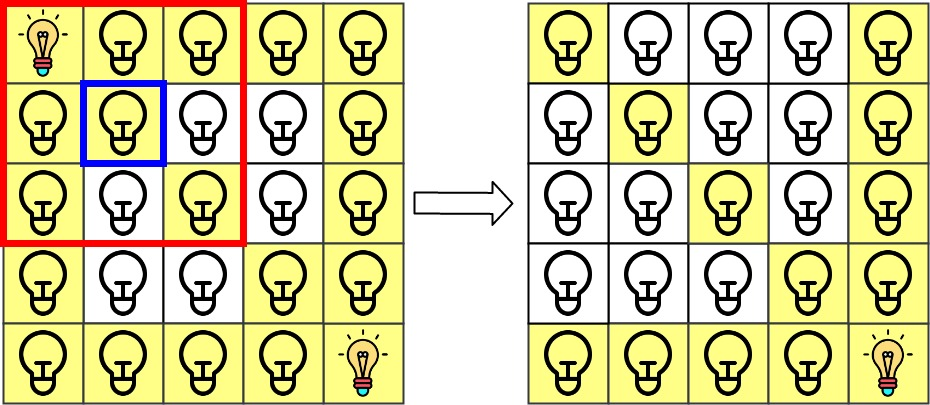
第 1 次查询检查 grid[1][0] 是否被照亮(蓝色方框)。该单元格没有被照亮,所以 ans[1] = 0 。然后,关闭红色矩形中的所有灯。
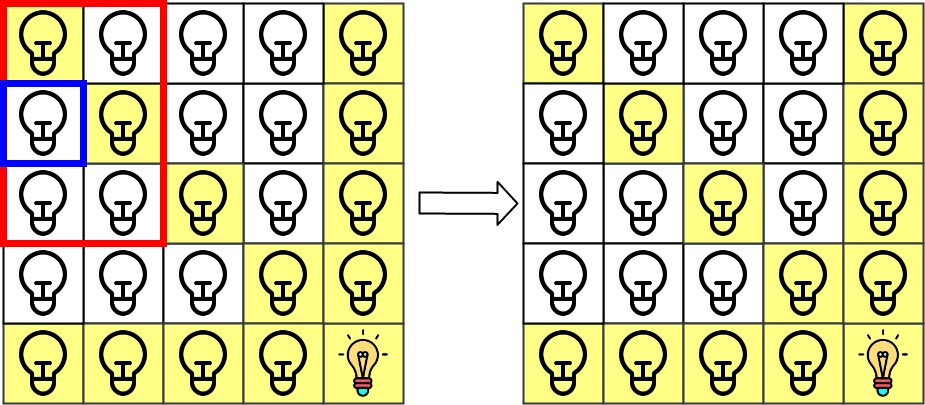
示例 2:
输入:n = 5, lamps = [[0,0],[4,4]], queries = [[1,1],[1,1]]
输出:[1,1]示例 3:
输入:n = 5, lamps = [[0,0],[0,4]], queries = [[0,4],[0,1],[1,4]]
输出:[1,1,0]提示:
1 <= n <= 10^90 <= lamps.length <= 200000 <= queries.length <= 20000lamps[i].length == 20 <= row_i, col_i < nqueries[j].length == 20 <= row_j, col_j < n
Python:
import collections
class Solution:
def gridIllumination(self, n: int, lamps: List[List[int]], queries: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
row, col = defaultdict(int), defaultdict(int)
dia, rdia = defaultdict(int), defaultdict(int)
aset = set()
for (x, y) in lamps:
if (x, y) not in aset:
aset.add((x, y))
row[x] += 1
col[y] += 1
dia[x-y+n-1] += 1
rdia[x+y] += 1
result = [0 for i in range(len(queries))]
for i, (x,y) in enumerate(queries):
if row[x] > 0 or col[y] > 0 or dia[x-y+n-1] > 0 or rdia[x+y] > 0:
result[i] = 1
for a in range(x-1, x+2):
for b in range(y-1, y+2):
if 0 <= a < n and 0 <= b < n and (a, b) in aset:
aset.remove((a,b))
row[a] -= 1
col[b] -= 1
dia[a-b+n-1] -= 1
rdia[a+b] -= 1
return resultJava:
class Solution {
public int[] gridIllumination(int n, int[][] lamps, int[][] queries) {
Set<List<Integer>> aset = new HashSet<>();
Map<Integer, Integer> row = new HashMap<>();
Map<Integer, Integer> col = new HashMap<>();
Map<Integer, Integer> dia = new HashMap<>();
Map<Integer, Integer> rdia = new HashMap<>();
for(int[] a: lamps)
{
List<Integer> arr = Arrays.asList(a[0], a[1]);
if(!aset.contains(arr))
{
aset.add(arr);
int x = a[0];
int y = a[1];
row.put(x, row.getOrDefault(x, 0)+1);
col.put(y, col.getOrDefault(y, 0)+1);
dia.put(x-y, dia.getOrDefault(x-y, 0)+1);
rdia.put(x+y, rdia.getOrDefault(x+y, 0)+1);
}
}
int[] result = new int[queries.length];
for(int k = 0; k < queries.length; k++)
{
int x = queries[k][0];
int y = queries[k][1];
if(row.getOrDefault(x, 0) > 0 || col.getOrDefault(y, 0) > 0 || dia.getOrDefault(x-y, 0) > 0 || rdia.getOrDefault(x+y, 0) > 0)
{
result[k] = 1;
}
for(int i = x-1; i < x+2; i++)
{
for(int j = y-1; j < y+2; j++)
{
List<Integer> temp = Arrays.asList(i, j);
if(i >= 0 && i < n && j >= 0 && j < n && aset.contains(temp))
{
aset.remove(temp);
row.compute(i, (key,v)->v-=1);
col.compute(j, (key,v)->v-=1);
dia.compute(i-j, (key,v)->v-=1);
rdia.compute(i+j, (key,v)->v-=1);
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
留言